

Interaction between civil society and the state is often a relevant area of tension. The conflict is usually associated with a high-profile event in a sensitive area for people (social obligations of the state, environment, culture, urban planning, political rights), when the balance of interests between society and the government is violated. Such conflicts are inevitable and constitute an important channel for feedback. But in order for the conflict to serve as a starting point of changes for the better and not to pass into the uncontrolled stage, the society and the governments need a working system of dialogue platforms to discuss substantive issues.
Today, the demand for upholding one’s interests is obviously growing, over several years, new civilian communities with an active lifestyle have emerged and strengthened. Most public organizations are required to interact with government bodies in one form or another.

Active citizens often have no experience of direct and constructive dialogue with the governments. Under these conditions, the civic chambers and councils get a chance for more intensive development as discussion platforms at which positions of the parties on controversial issues are discussed and coordinated. Ideally, such intermediary institutions should become a permanent interactive channel for escalating information to supreme authorities on what really worries citizens on the local level. In this way, they can ensure the continuous and efficient engagement of citizens in the discussion of decisions, and contribute to the creation of co-management mechanisms.
It is no less obvious that the “pocket” intermediary institutions dependent on local governments are not able to provide full dialogue and search for a compromise, and this leads to discontent and a new conflict.
An important form of interaction between citizens and the state are the petitions of citizens. In 2018 (as of November 21, 2018), the Civic Chamber of the Russian Federation received 29,411 petitions from citizens. They are mainly concerned with social sphere and housing and communal services, the work of judicial and law enforcement systems. Among the main problems are the disposal of garbage, the availability and quality of medical and social expertise services, the protection of voters’ rights. The petitions come both through the Chamber’s website and through hotlines on the most sensitive issues.
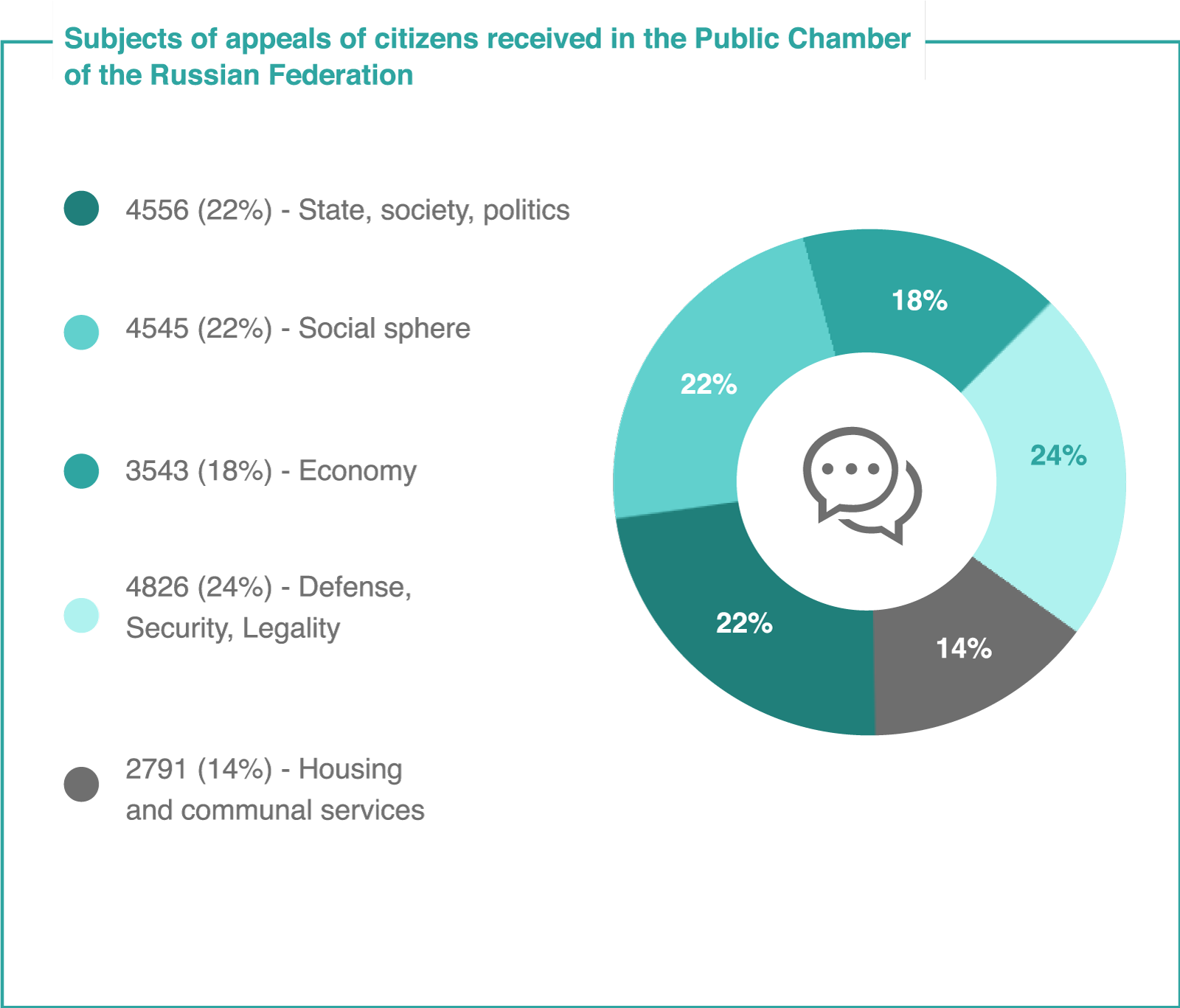
Source: Civic Chamber of the Russian Federation
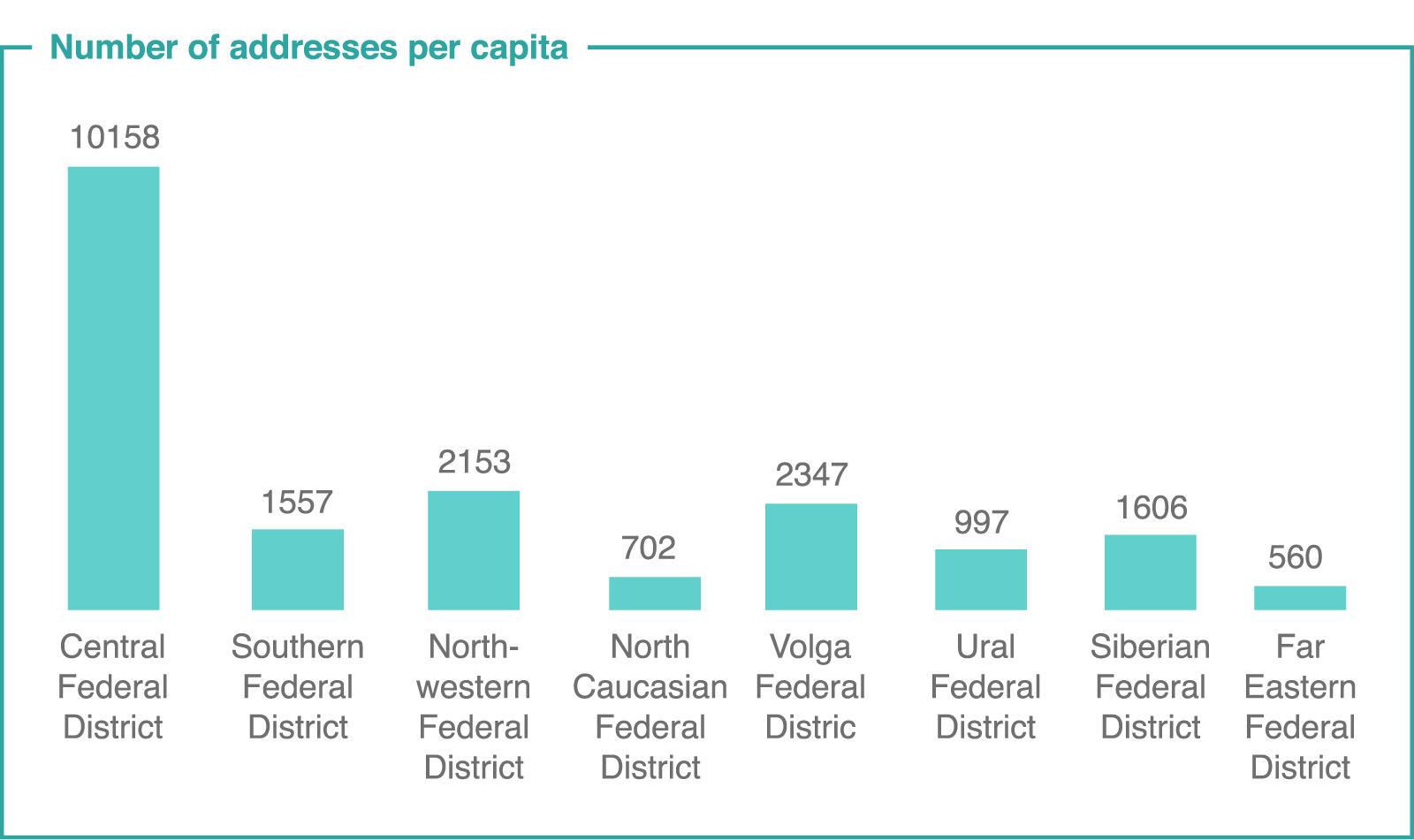
Source: Civic Chamber of the Russian Federation

In the regions, civic chambers are becoming the leading platform for public-state dialogue.
Civic chambers exist primarily to ensure the interaction of individual citizens and their associations with the authorities. Today, these institutions are also involved in the examination of bills, carry out public scrutiny, are involved in the formation of regional public councils. In some subject regions of the Federation, civic chambers are vested with the right of legislative initiative.
About ten years have passed since the system of civic chambers in the regions started to be formed. During that time most chambers have found their place in the public space of the regions. In early 2017, the Federal Law of the Russian Federation of June 23, 2016 No. 183-FZ “About the general principles of the organization and activities of civic chambers of subject regions of the Russian Federation” entered into force. They feared that as a result of its adoption the activities of civic chambers can assume a uniform and monotonous nature of “one size fits all”. In fact, the expert examinations held by the Civic Chamber of the Russian Federation in 2018 showed that the chambers in the regions differ markedly in the priorities of their activities. In some regions, at the site of the chamber, it is possible to implement interesting initiatives, the experience of which is applicable in other regions. For example, the Civic Chamber of Kirov Region is most active in the sphere of public control, a working group on control in the field of road construction is constantly working and includes representatives of the public and the supporting university. Another example is the Website of the Civic Chamber of Ulyanovsk Region, specific problems of local life are examined at weekly meetings featuring public figures, experts, representatives of municipal and regional governments. In Vologda Region, the local Chamber oversees the activities of municipal chambers. But, in some regions, survey participants could not name a single significant initiative and project of a regional chamber; not all chambers managed to secure the status of sites, where active citizens have the opportunity to reach out to power41 #WHAT IS WRONG: results of regional studies of dialogue//Center of the applied research programs, 12.06.2018: http://www.prisp.ru/analitics/750-chtonetak-analytics..

According to the annual survey held by the Civic Chamber of the Russian Federation at the “Community” Forum, the number of NPOs employees and public activists who in in this or that way participate in regional civil chambers is gradually increasing, but most of the third sector representatives do not interact with chambers in the regions. The participants of the forums, which already have experience of interaction with civic chambers, are mostly positive.
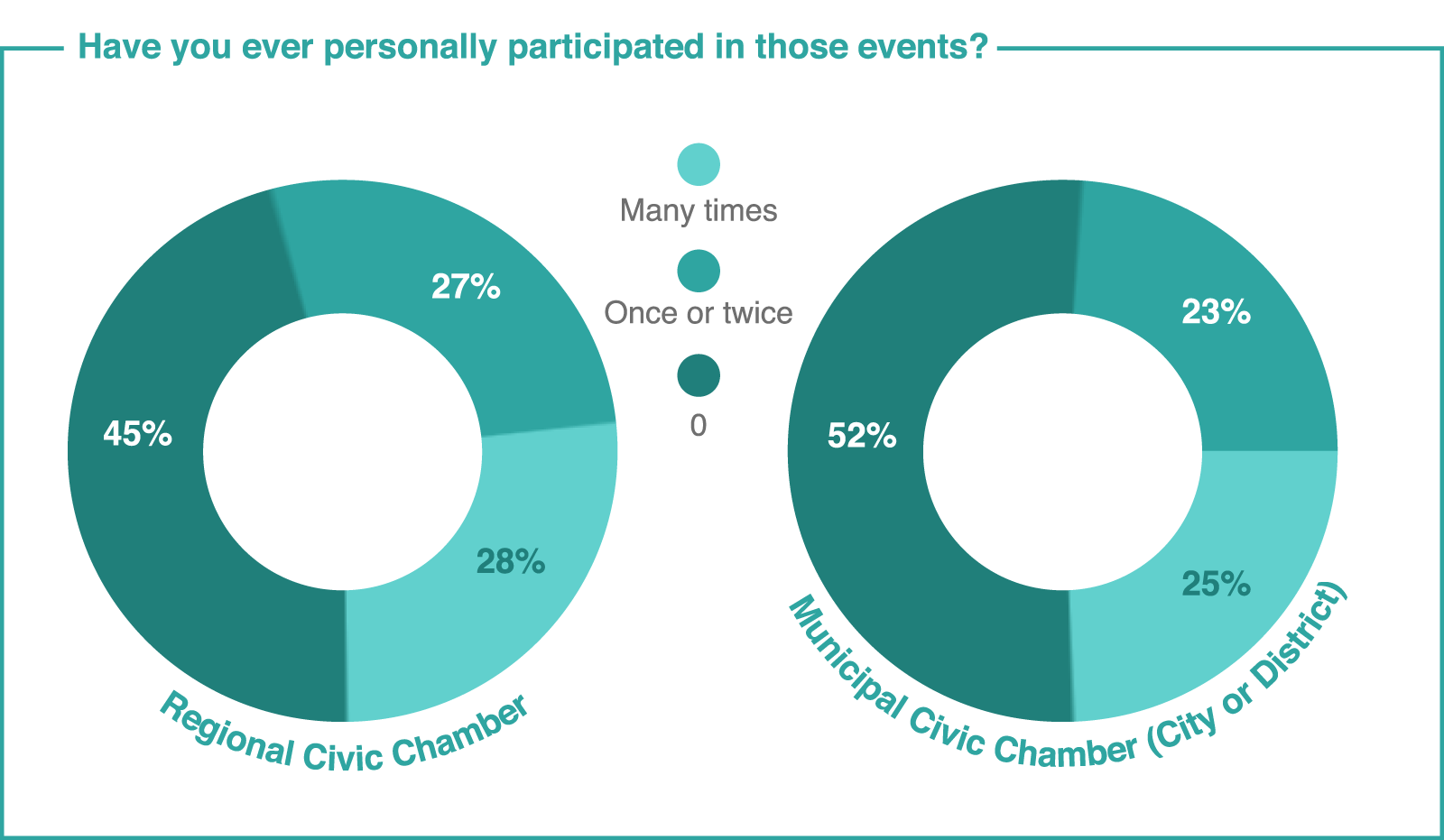
Source: Civic Chamber of the Russian Federation42 Poll of the participants in regional and final “Community” Forum in 2018. 774 people took part in the survey.
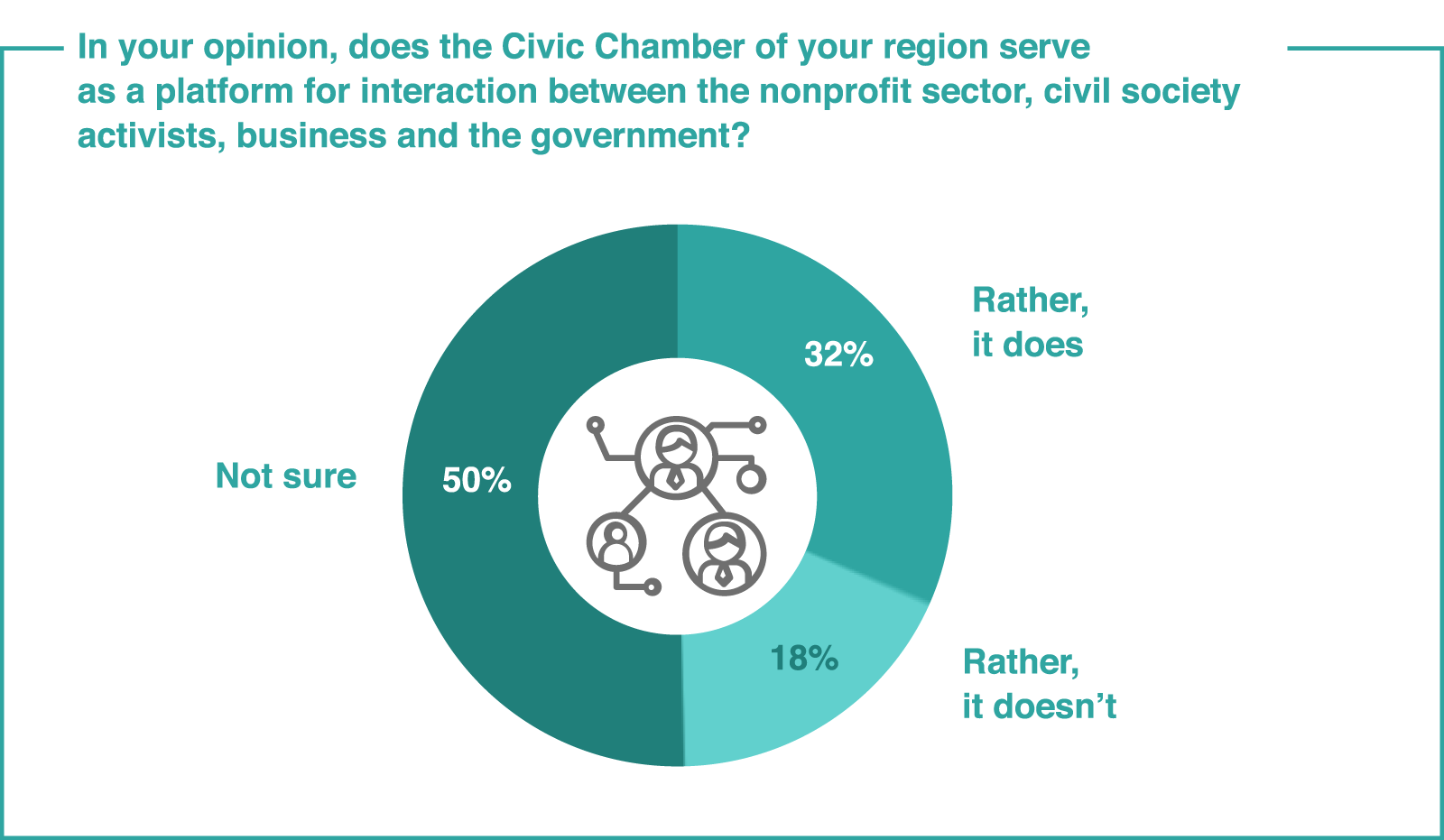
Source: Civic Chamber of the Russian Federation43 Description of the survey, see link 42.
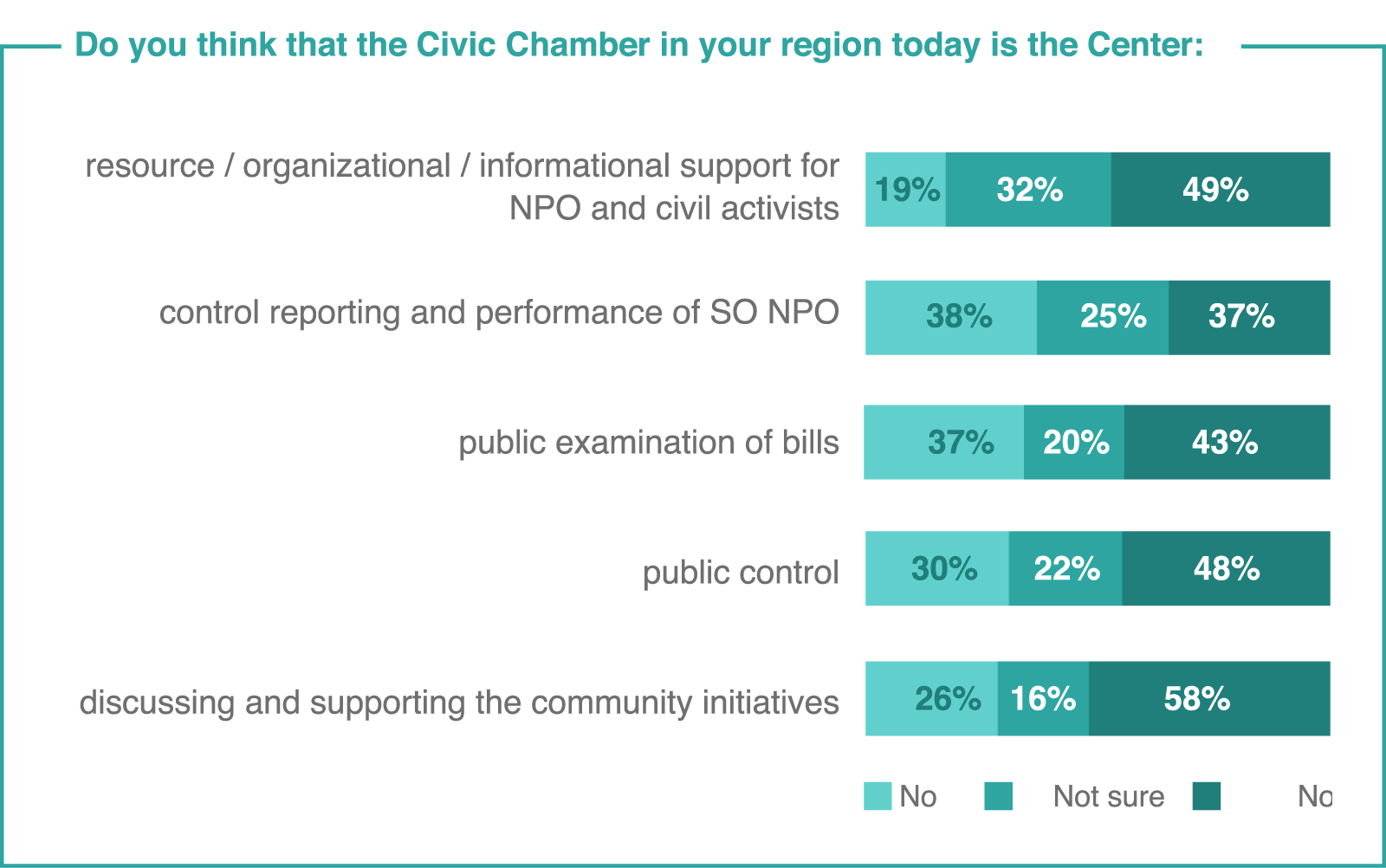
Source: Civic Chamber of the Russian Federation44 Description of the survey, see link 42.
In 2018, the Civic Chamber of the Russian Federation held a survey “Information support for the activities of civic chambers of the subject regions of the Russian Federation”, which was attended by members of regional civil chambers45 Survey “Informational accompaniment to the activities of civic chambers of the subject regions of the Russian Federation” was held from May 18 to June 5, 2018 at the initiative of the Commission for the Development of the Information Society, Mass Media and Mass Communications of the Civic Chamber of the Russian Federation. The study involved 75 civic chambers.. The respondents named official websites the main source of information about the activities of regional chambers, social media were mentioned much less frequently, only 21.3% of respondents believe that they know the chamber in the region well. Regional Civic Chamber are not always active.
Since 2015, the Civic Chamber of the Russian Federation held separate monitoring of the openness and transparency of the websites of regional civic chambers. In general, the capability of sites is on a rise, and you can directly send a message to 58 of them. At the same time, many sites do not have section “Announcements”, only 27 sites have a special section dedicated to the examination of bills (on the websites of the three Chambers the section is not filled at all), and the draft conclusions submitted to the authorities are available on 15 sites. The sites of civic chambers of the Republic of Tatarstan, Kirov Region, Krasnodar Territory, Yaroslavl Region and Chelyabinsk Region became the leaders of monitoring in 201846 Monitoring sites of regional civic chambers: improving the quality of public-state dialogue // Center for Applied Research Programs, 26.10.2018: http://www.prisp.ru/analitics/1182-komkov-monitoring-saitov-reg-op-2610..
The credibility and authority of the Civic Chamber largely depends on the position of the regional leadership – without engagement of authorities, the dialogue has no sense. Regional governments sometimes lack the culture of a dialogue leading to dangerous rupture with civil society activists. On the one hand, officials are afraid of activists, on the other hand, activists are suspicious of the authorities. In order to speed up the dialogue of active citizens and the governments at the regional chambers site, to reduce the distance between the bureaucracy and public activists, one can say to force officials to interact with public figures, the Civic Chamber of the Russian Federation initiated #What is wrong? project in 201747 The project involves the Center for Applied Research and Programs (ARP Center) and the Russian Reporter magazine.. The project organizes discussion platforms featuring activists, governments, media and entrepreneurs. #What is wrong? street polls are held in order to identify the “people’s agenda” of cities and present this agenda to the officials and activists. In 2018 the project embraced 11 regions (15 regions in total in 2017-2018).
The credibility of the Civic Chamber is built on specific projects, coverage of the Chamber’s activity in the media, clear position on resonant issues of local agenda, and most importantly, on the Chamber members and leaders of public opinion. Many chambers are attended by people who come rather for status not related to the third sector (mainly entrepreneurs, directors of large enterprises, former civil servants). At the same time, public activists are simply out of sight of the regional Civic Chamber, they implement their projects without any involvement of the chamber. Almost every region has at least a few people, whose activities are well visible.
Such activists can play a positive role and bring something new to the activities of civic chambers. As it was noted in the Report of the Civic Chamber of the Russian Federation for 2017, one of the ways to strengthen the independence of public chambers in the regions can be the engagement of the Civic Chamber of the Russian Federation in their formation through legislative consolidation of the quota of the Civic Chamber of the Russian Federation in the formation of each regional chamber. If the Civic Chamber gets an opportunity to recommend two or three people to become part of the regional Civic Chamber, it will be useful both for the regions and for civil society as a whole48 Quotas for the disloyal in civil chambers can be introduced // Center for the Applied Research and Programs, 04.08.2018: {2>http://www.prisp.ru/analitics/897-kanaeva-op-sostav-0308..
In addition, the activity of the Chamber depends on funding. Even for the organization of meetings, especially public control events, not to mention larger-scale projects, a certain material base is needed. As far as public expertise is concerned, it is necessary to attract qualified experts. These are small tools required for the workflow. At the moment there are no legal provisions on budget financing of civic chambers of the subject regions of the Russian Federation. It will contribute to consolidating the independence and productivity of civic chambers.
The Council of the Cvic Chamber of the Russian Federation on interaction with civic chambers of the subject regions (Council of the Civic Chambers of Russia) continues its activities. The Council coordinates the engagement of regional chambers in monitoring the implementation of the Address of the President of the Russian Federation to the Federal Assembly and the May Decree of the President of Russia dated May 7, 2018 No. 204 “On the national goals and strategic objectives of the development of the Russian Federation for the period up to 2024”, as well as the formation of public councils on independent quality assessment of the conditions of services provision under the Federal Law No. FZ-392 dated December 5, 2017 “On Amendments to Certain Legislative Acts of the Russian Federation on Improving the Independent Evaluation of the Quality of Service Conditions by Organizations in the Sphere of Culture, Health, Education, Social Services and Federal Institutions of Medical And Social Expertise”. This is a direct objective of civic chambers. These projects enhance their credibility, let them consolidate the role of mediator between the governments and civil society.
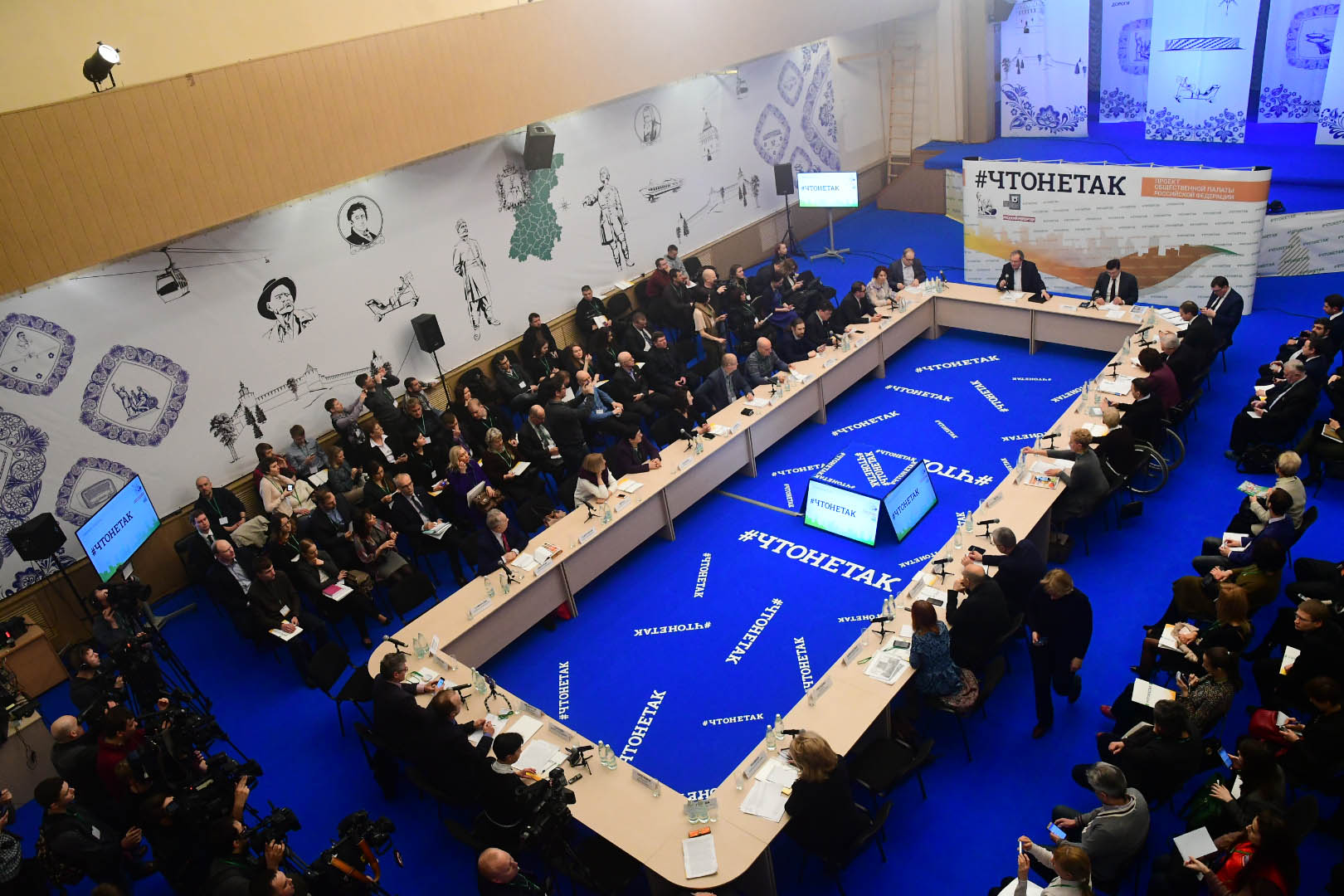

In order to speed up the dialogue of active citizens and authorities at the regional chambers site, to reduce the distance between the bureaucracy and public activists, one can say to force officials to interact with public figures, the Civic Chamber of the Russian Federation initiated #What is wrong? project in 2017
In many regions, municipal civic chambers (councils) are actively developing. These dialogue platforms are very close to the population, they discuss issues directly related to the residents. Therefore, people are often more actively involved in this work. At the same time, the activities of such chambers are poorly regulated by the law, and the order of formation in regional laws, as a rule, is not specified. A special section was organized at the “Community” Forum in Kaliningrad for a substantive discussion of the development prospects of municipal civic chambers. The participants, most of whom were just municipal community members, appealed to members of the Сivic Chamber of the Russian Federation to initiate Federal normative legal act or model provisions on procedure formation and activities of the municipal public chambers and councils. In addition, they spoke in favor of developing a rating system for the activities of public councils at all levels, which will ensure correct goal-setting, replicate best practices, and increase attention to the activities of public councils.
In the lead-up to the “Community” Forum, the first contest of municipal civic chambers (councils) of the North-West Federal District was held. They managed to identify the noteworthy projects. For example, the council of the Yb rural settlement of the Syktyvdinsky District of the Komi Republic became the best municipal public council of the rural territory: the first stage of the Finno-Ugric Ethno-Cultural Park was put into operation with the engagement of members of Ybitsa public council. At the section, a proposal was made to hold a federal contest for municipal public chambers and councils. One cannot help but notice that often there is no interaction of regional and municipal civic chambers.
It is significant that on the websites of regional chambers there is often no information about chambers in municipalities.
The Federal Law of 21 July 2014, No. 212-FZ “On the Fundamentals of Public Control in the Russian Federation” states among the subject regions of public control the Civic Chamber of the Russian Federation, civic chambers of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation, civic chambers (councils) of municipalities and public councils attached to federal executive bodies, public councils with legislative (representative) and executive bodies of state power of the subject regions of the Russian Federation.
So far it is impossible to say that an effective system of public control has developed in our country. Nevertheless, in some areas there are significant examples of public control that allow you to change the situation for the better.
In 2018, a major breakthrough in the development of public control and a system of civic chambers in the regions was the creation of a large-scale election observation system. In accordance with the Federal law No. 374-FZ as of December 5, 2017 on amendments to the Federal Law on the election of the President of the Russian Federation, the Сivic Chamber of the Russian Federation and the civic chambers of the regions have been granted the right to send observers independent from political parties to monitor the electoral process at the polling stations. In four months, the system of public chambers held more than 750 events throughout the country: observer forums, round tables, meetings of representatives of NPOs, and observers training.
At the request of the Civic Chamber of the Russian Federation and civic chambers in the regions, the election was monitored by 1866 federal, regional and municipal public organizations from all regions of Russia and about 150 thousand observers.
Observers from the civic chambers were present almost at every polling station. This ensured the transparency of the elections, cases of fraud and irregularities were numerous.
The Situation Center for Public Monitoring of Presidential Elections worked within the Civic Chamber of the Russian Federation. During the day, from 23:00, March 17 to 23:00, March 18, the volunteers of the Situation Center were in touch with public observers. 300 volunteers were involved in the work of the center. 1723 reports of violations were received, of which about 80% violations were recorded.
Civic chambers became the backbone of the new system of public observation at the elections, the project largely changed their political weight in the regions. In fact, in a few months a new significant public institution was created, initiated by civil society and supported by a new legislative framework. It became apparent that the Civic Chamber in the regions have serious potential.

The next stage was the deployment of a regional system of the election public observation. Russian President Vladimir Putin signed the Federal Law of July 3, 2018 No. 184-FZ “On amendments to the Federal Law “On basic guarantees of electoral rights and the right to participate in referendums of citizens of the Russian Federation”, which allowed the Civic Chamber of the Russian Federation and regional civic chambers send observers to election commissions at regional and local elections. Now the constituent entities of public control, the federal and regional civic chambers, and through them any public organizations, volunteers and active, not indifferent citizens of Russia have the right to attend the polling stations and monitor the elections that are held in the country. Regional civic chambers have the right to send observers to the election commissions of the relevant subject region of the Russian Federation.
Observation of the elections with the engagement of the general public took place on a single voting day in the subject regions of the Federation, on September 9, as well as in the second round of voting of the governor election in several regions. In 22 regions, including Moscow and the Moscow region, direct elections of governors took place, in 4 subject regions of senior officials elected deputies of the legislative assemblies. In 16 regions, residents chose deputies of regional assemblies. In addition, it’s been about 6 thousand municipal elections49 Observers from the public chambers will be able to participate in regional elections//Rossiyskaya Gazeta, 27.06.2018: https://rg.ru/2018/06/27/nabliudateli-ot-obshchestvennyh-palat-smogut-uchastvovat-v-regionalnyh-vyborah.htm..
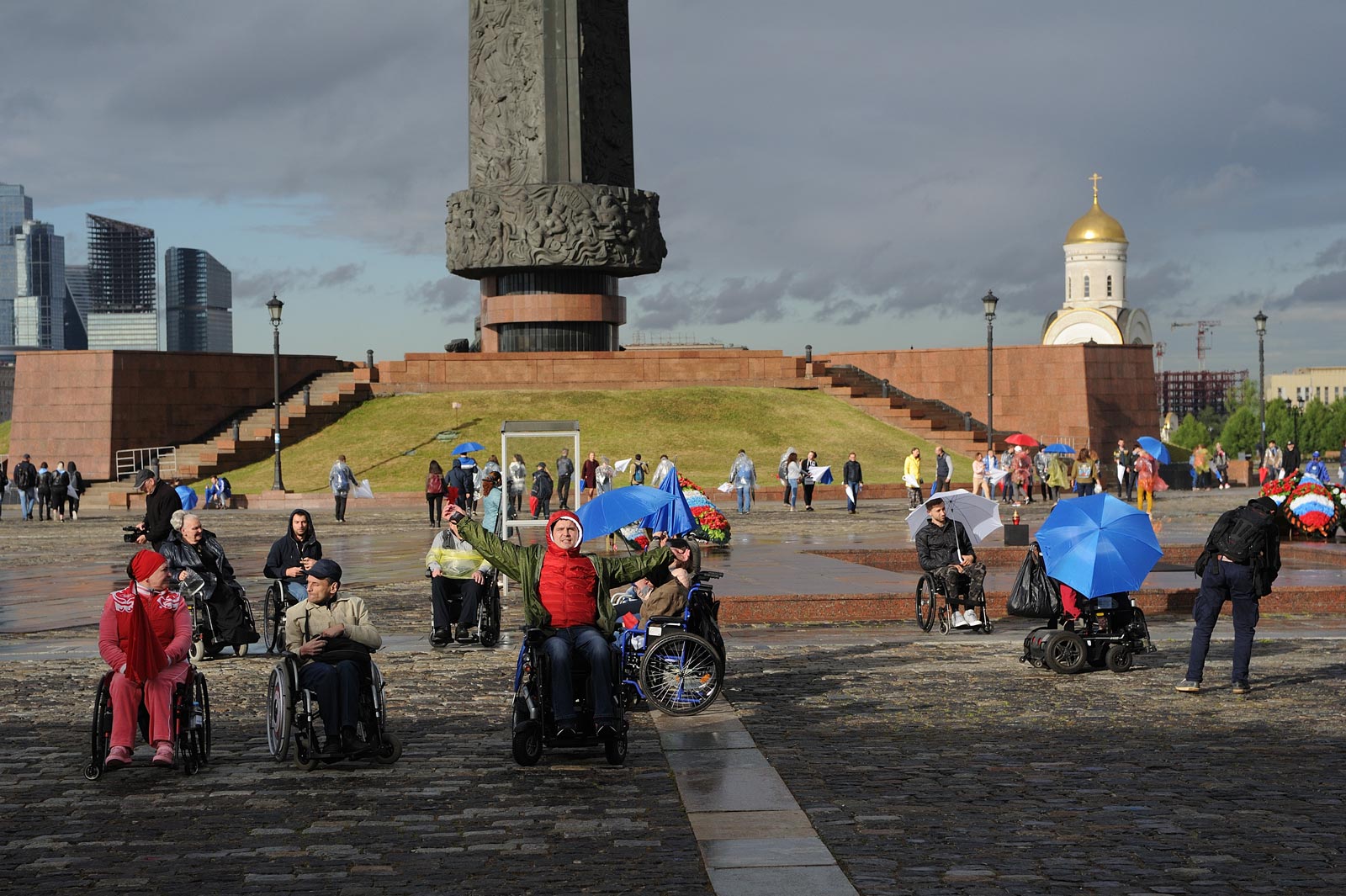

As a result of the active work of social activists in this area, a kind of revolution took place: On March 29, 2018, the Government of the Russian Federation issued Decree No. 339 On amendments to the Rules for recognizing a person as a disabled person”, thanks to which the methods of examination and re-examination of disability were considerably simplified.
Just as in the election of the President of the Russian Federation, the Situation Center for Public Observation of Elections worked within the Civic Chamber of the Russian Federation. The center’s volunteers online kept in touch with public observers from different parts of the country. The incoming information was published on a special site общественныйнаблюдатель.рф.
Not all regions managed to adopt their own laws on public election observation by September 9. Thus, only the civic chambers in Moscow, Republic of Kalmykia, Primorsky Territory, Altai Territory, Amur, Moscow, Nizhny Novgorod, Rostov, Samara, Ulyanovsk, Kemerovo regions, as well as Chukotka Autonomous Region were able to send observers to polling stations in accordance with the adopted regional laws. In other regions, observers from civic chambers were sent to polling stations according to quotas provided by candidates and political parties.
In total, 30,000 observers from civic chambers followed the elections on a single day of voting throughout the country. The elections on September 9 showed significant progress as compared to previous elections in the regions, including the elections to the State Duma in 2012: there were noticeably fewer complaints about the quality of the elections.
In the sphere of public control there are other significant results. In October 2017, the Civic Chamber of the Russian Federation opened a hotline on the activities of medical and social expertise. Over the period of the hotline work (from October 2017 to January 2018), it received about a thousand messages. The most frequent reason for address was the refusal to assign disability or its removal. It concerns tens of thousands of citizens who don’t have now to pass the examination anew every year.
Interesting practices in the field of public control appear in some regions with the engagement of civic chambers.
In Vologda Region, a system of public control over the use and maintenance of roads has been created, an information field has been formed indicating the ownership of roads and a base to which any person can send the information about a fault in one or another section of the road50 The renovated composition of the public council started its work at Rosavtodor // Website of the Civic Chamber of the Russian Federation,20.06.2018: https://oprf.ru/press/news/2018/newsitem/45768.. The Commission on Social Infrastructure and Housing and Public Utilities of the Сivic Chamber of the Novgorod Region conducts a rating of management organizations in the housing and utilities sector — HUK (the worst management company). In Arkhangelsk Region, people’s inspectors in the housing and utilities sector worked for seven years51 Spot building, overhaul and emergency gangs: the people’s inspectors of Pomorye told about housing and public utilities troubles of the northerners // Arkhangelsk online 29.RU, 19.04.2018: https://29.ru/text/gorod/421789822164994.html https://29.ru/text/gorod/421789822164994.html.. Each institution is evaluated by patients, the criteria include openness, comfort, waiting time, friendliness of employees. Over the past year, six physicians-in-chief received disciplinary sanctions on the proposal of the public council52 “Public control” is a two-way road ”// “Open ”, Issue No. 14 (809) of April 9 – 16, 2018:https://www.opengaz.ru/stat/obshchestvennyy-kontrol-eto-doroga-s-dvustoronnim-dvizheniem.. In Orenburg region, due to the public control system, it was possible to noticeably improve the work of medical and social expertise, the situation in which was quite difficult53 Revolution in disability certification – public control in action // Website of the Civic Chamber of the Russian Federation, 25.04.2018: https://oprf.ru/press/news/2018/newsitem/45055.
The Civic Chamber of Stavropol Territory54 The official site of the Public Chamber of Stavropol Territory.. http://opsk26.ru/2018/11/05/%D0%B7%D0%B0%D0%BA%D0%BE%D0%BD%D0%BE%D0%BF%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%B5%D0%BA%D1%82%D1%8B-%D0%BA%D0%BE%D1%82%D0%BE%D1%80%D1%8B%D0%B5-%D1%82%D0%BE%D0%BB%D1%8C%D0%BA%D0%BE-%D0%B2%D0%BE-%D0%B2%D1%80%D0%B5%D0%B4/ conducts systematic work on public control over the preservation and rational use of the natural potential, the unique therapeutic and health properties of a specially protected ecological-resort region of federal importance Caucasian Mineral Waters, including in the context of the execution of the instructions of the President of Russia on the development of a sanatorium development strategy resort complex of the Russian Federation55 Clause 1a of the List of Instructions of the President of the Russian Federation of September 19, 2016 No. Pr-1817.. The results of this work were, in particular, taken into account by the Government of Russia in the development and adoption of the strategy, approved at the end of November 201856 Order of the Government of the Russian Federation of November 26, 2018 No. 2581-r. http://www.garant.ru/products/ipo/prime/doc/72013422/...
An interesting initiative is being implemented in Chelyabinsk Region, where a peculiar center of public control functions — an inter-commission working group that deals only with issues of public control. Volunteers who are trained and receive the status of public inspector are involved in conducting public inspections.
One of the areas of public control is the public examination of draft regulatory acts. Evaluation of legislative initiatives is one of the most important tasks of civil society institutions, which allows improving the quality of adopted laws not only from a legal point of view, but on the basis of their compliance with the expectations and needs of society. For this work, we need certain resources, first of all the expert ones. Therefore, public expertise is carried out, primarily, at the Website of the Civic Chamber of the Russian Federation, as well as a number of regional chambers. In 2018, the Civic Chamber of the Russian Federation held 30 public examinations, 26 of them in the zero reading format. Two bills were supported, taking into account the comments of 15 bills, and two bills were not supported (as of 1.18). From June 2017 to May 2018, following the resolutions of the Civic Chamber of the Russian Federation, four resolutions and 66 recommendations were sent to the governments.

Public councils under federal executive bodies are an important institution of public control. The councils is formed by the Civic Chamber of the Russian Federation on a competitive basis; the right to nominate members to the public councils has been received by specialized non-profit organizations.
Since 2017, the reset of the system of public councils began. The main idea is that members of public councils should act as guides of the “people’s agenda”, guided not only by professional knowledge and skills, but, first and foremost, by the requests that the population has. Public councils are called upon not only to discuss the initiatives of the ministries, but to encourage them to deal with essential problems. Moreover, public councils can influence the personnel policy of the department, participate in certification procedures, improve the skills of personnel, and work with citizens.
As part of this process, a number of technical innovations have been implemented in order to make the competitive selection procedure more transparent. A single portal of public councils os.oprf.ru was created at, electronic platform for the engagement in the contest of candidates for public councils was built (with electronic registration, personal account). All decisions, even on replacements of retired members, are taken during a full-fledged contest; in preparation for voting, in-person meetings of the leadership of the Civic Chamber of the Russian Federation with candidates for council members are held. In 2017, the Civic Chamber developed and adopted a regulation for evaluating the efficiency of public councils.
Most of the first organizational, meetings of public councils are held at the Website of the Civic Chamber of the Russian Federation, work is underway to form a “popular agenda” of their meetings and to select resonant issues for the activities of the councils. In addition, the Civic Chamber initiates interagency cooperation: joint meetings of public councils were held at Federal Agency on Technical Regulating and Metrology and RusAccreditation, Federal Air Transport Agency and Federal Tourism Agency, a forum of passengers was held with the involvement of interested parties (airlines, insurers, passenger representatives, the Federal Customs Service of Russia, Federal Transportation Inspection Service, community activists). In November 2018 the Website of the Civic Chamber of the Russian Federation, the Public Council under the Federal Forestry Agency Public Council launched the All-Russian forum “Forest: dialogue of society and the government for the sake of preserving the life environment.
During its first year the Civic Chamber of the VI convocation held 20 contests to elect the members of the public councils under a new standard The average contest was five people per vacancy, the highest contest was 21 people at in public Council under the Federal Anti-Monopoly Service. As a result, five public councils are fully formed, five are at the final stage of formation, ten are going through the stage of analyzing and checking candidate profiles57 As of November 1, 2018 year..
As practice has shown, many of the previously formed councils are either late with the discussion, or do not even consider issues causing a great public outcry. In 2019, it is planned to early terminate the powers of several public councils that continue to work outside the civil society agenda58 “We are not bosses to you, but we must coordinate our activities with you“ – Valery Fadeev // Website of the Civic Chamber of the Russian Federation, 17.10.2018: https://www.oprf.ru/press/news/2018/newsitem/46953..

In the near future, it is necessary to develop clear criteria for the selection of normative legal acts and projects for public control, as well as criteria for the division of expert work and the assessment of public importance. The agenda of the work of councils automatically, according to the regulations, includes a large number of issues that are of no interest to civil society organizations, or those for which representatives of civil society are unable to have a professional position. At the same time, there is often no time left for in-depth consideration of issues that are fundamentally important for civil society, including those that cause relevant social conflicts – for instance, the issue of recycling solid household waste has never been considered by the Ministry of Environment Council. At the same time, a certain formalization of the activities of the councils is also necessary: the results of the discussions should take a comprehensive form of specific proposals and initiatives addressed to the leadership of the department, with the possibility of further monitoring their implementation. In the course of discussions in the Civic Chamber of the Russian Federation, a suggestion was made that many of the shortcomings in the activities of public councils could be eliminated by recognizing the public councils at government bodies as working bodies of the Civic Chamber, which must meet and report on the work done at regular intervals.
In many regions of the Russian Federation, a system of public councils has been created under regional executive authorities. According to a survey conducted by the Civic Chamber of the Russian Federation in 2018, the majority of participants in the “Community” Forums are aware of the activities of public councils in their regions, more than 30% have experience of interacting with them.

Source: Civic Chamber of the Russian Federation59 Description of the survey, see link 42.
It is necessary to ensure interaction of civic chambers and public councils with regional governments. At the federal level, it exists because the Civic Chamber of the Russian Federation participates in the formation of the public councils. However, at the level of the subject regions of the Federation, instead of constructive and well-coordinated work of activists, it is sometimes possible to observe the confrontation between civic chambers and public councils. The latter often stand up for the authorities in which they are formed. In addition, the status of other public structures under regional governments is not clear: councils for interaction with business entities, expert councils, etc. It’s time to define more clearly the place of these bodies in the system of public control.
An important aspect of public control is control over the detention of persons in places of deprivation of liberty. As of November 1, 2018, there were 571,007 people in penitentiary institutions. The staff number of the Penal Enforcement System (PES), funded from the federal budget is 295,967 people60 Official website of the Federal Penitentiary Service of Russia http://fsin.su/structure/inspector/iao/statistika/Kratkaya%20har-ka%20UIS/.. That is, for two prisoners there is one full-time employee.
In accordance with Federal law No. 76-FZ of 10 June 2008 “On public monitoring of human rights in places of detention and on assistance to detainees”, the Civic Chamber of the Russian Federation is empowered to form public monitoring committees and to suspend and terminate the powers of their members. Thus, unlike other world analogues, such as the UK or France, where inspectors are appointed by the executive governments, the members of the public monitoring committees in our country are approved by the public. At the same time, they fulfill their voluntary commitments on a voluntary basis in their spare time, often using their personal vehicles and means of communication.
Today the country has 83 public monitoring committees61 Information on PMC/Website of the Civic Chamber of the Russian Federation: https://www.oprf.ru/1449/2133/1536/1857/.. During the year of work of the Civic Chamber of the Russian Federation of the current composition, the rotation of the PMC members took place in 13 regions. In 2018, members of the Civic Chamber of the Russian Federation held 62 events of various formats dedicated to the situation in this sphere.
from December 2017 to February 2018, PMC were rotated in 6 subject regions of the Russian Federation (Altai Republic, Zabaikalsky Territory, Kamchatka Territory, Nenets Autonomous District, Chukotka Autonomous District, Yamalo-Nenets Autonomous District).
Within the framework of the said procedure, the PMC in Nenets Autonomous District, Chukotka Autonomous District, Yamalo-Nenets Autonomous District were not formed in the authorized composition. 16 members of the PMC were appointed.
from January to April 2018, PMC were rotated in 2 subject regions of the Russian Federation (the Republic of North Ossetia – Alania, Vologda Region).
Under this procedure, 16 members of the PMC have been appointed.
from March to May 2018, the rotation of the PMC was held in 5 subject regions of the Russian Federation (Krasnoyarsk Territory, Jewish Autonomous Region, Nenets Autonomous District, Chukotka Autonomous District, Yamalo-Nenets Autonomous District).
Within the framework of this procedure, the PMC in Nenets and Chukotka Autonomous Districts were not formed in the authorized composition. 35 members of the PMC were appointed.
Source: Civic Chamber of the Russian Federation
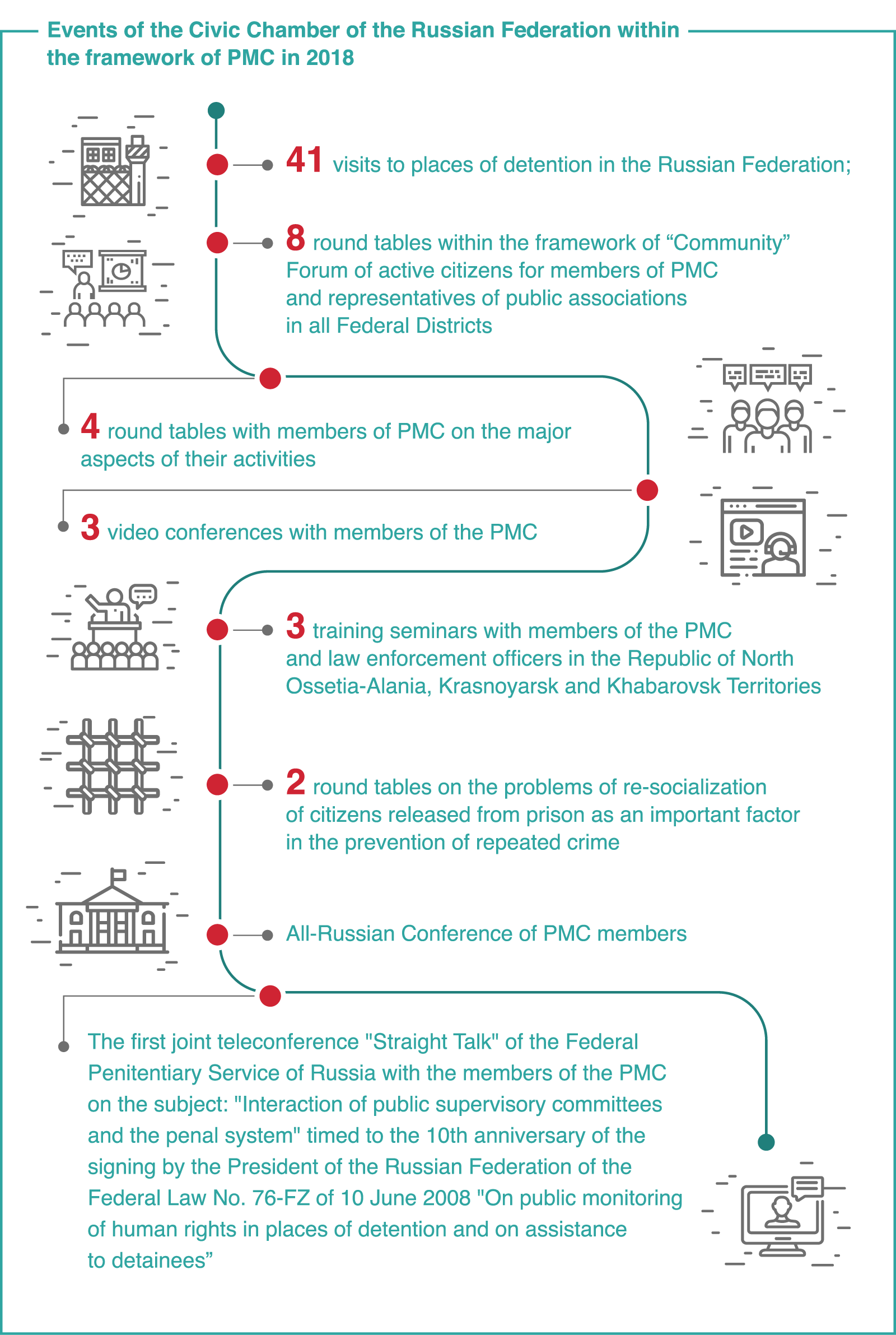
In particular, one of the most pressing is the issue of resocialization of convicts. There is no single legislative framework in this area. Proposals on the establishment of a coordinating council aimed at rehabilitation and adaptation of prisoners were discussed at the Website of the Civic Chamber of the Russian Federation. In this case, the regional PMC can extend their powers and join the work on re-socialization of persons released from prison, as provided in the Federal Law № 76-FZ62 Rehabilitation and social adaptation of convicts //Website of the Civic Chamber of the Russian Federation, 25.01.2018: https://www.oprf.ru/press/news/2018/newsitem/43729..

The Civic Chamber of the Russian Federation pays special attention to projects of support to women released from prison settlements63 “Step into new life: return to normal life for women released from a prison settlement//Website of the Civic Chamber of the Russian Federation, 29.06.2018: https://www.oprf.ru/1449/2133/1536/newsitem/45871., working with the families of convicts, in the first place with their children. In February 2018, the social rehabilitation center for women “Vera” opened in FSU Correctional Colony No. 28 of the Federal Penal Service Department of Russia in Volgograd Region64 Maria Kannabikh presents Vladimir Icon of the Mother of God to the “Faith” center as a symbol of a new free life// Website of the Civic Chamber of the Russian Federation, 16.02.2018: https://www.oprf.ru/1449/2133/1536/newsitem/44080.. In April 2018, the rehabilitation center for convicted women65 Rehabilitation center for convicted women opened in Buryatia // Social Information Agency, 12.04.2018: https://www.asi.org.ru/news/2018/04/12/ulan-ude-reabilitatsionnyj-tsentr-dlya-osuzhdennyh-zhenshhin/. was established in the Republic of Buryatia. On October 10, 2018, the World Mental Health Day, the Civic Chamber of the Russian Federation opened Aurora rehabilitation center in the FSU Treatment and Correctional Facility No. 7 of the Federal Penal Service Department of Russia in the Chuvash Republic in the town of Tsivilsk within the framework of the Partnership Territory project. This is the only correctional institution in Russia for the custody, treatment and rehabilitation of convicted women with alcohol and drug addiction66 Maria Kannabikh opens rehabilitation center for convicts in Chuvashia//Website of the Public Chamber of the Russian Federation, 12.10.2018: https://www.oprf.ru/1449/2133/1536/newsitem/46879.. The next step in the re-socialization of convicted persons should be a project to open such a center for convicted men. The Civic Chamber of the Russian Federation believes it necessary to pay special attention to the development of employment in prisons and after the release of citizens. For example, in the form of tax remissions for business organizations hiring former convicts67 Rehabilitation and social adaptation of convicts//Website of the Civic Chamber of the Russian Federation, 25.01.2018: https://www.oprf.ru/press/news/2018/newsitem/43729..

Besides these social control regular activities in the field of carried out at the Website of the civic chambers, councils and PCS, new initiatives, which involved civil activists and just partial citizens. As a rule, they are situational and linked with emergencies or hot conflicts. So, after the tragic fire in the shopping and entertainment center “Winter Cherry” in Kemerovo on March 25-26, 2018, public activists have joined the mass inspection of shopping centers, schools and other public places across the country. The Civic Chamber of the Russian Federation encouraged public observers to participate in the control of fire safety in crowded places. And people have responded to this appeal: for example, Ryazan residents themselves organized testing of trading centers of the city for their safety. Moreover, to coordinate their actions, they created a special public “Check of Ryazan shopping centers after the tragedy in Kemerovo” in the social network” “VKontakte”68 After the tragedy in Kemerovo TC checks will be held across entire Russia//RIA Novosti, 26.03.2018: https://ria.ru/incidents/20180326/1517320850.html. And activists from St. Petersburg during the inspection in the shopping centers “Peak” and “Sennaya” at Sennaya Square found deficiencies that was removed after their feedback69 Activists checked fire safety in shopping centers: there are complaints//Main regional news 12.04.2018: https://sankt-peterburg.glavny.tv/news/114705. According to Moscow activists, who also took part in such work in the capital, violations were found in 40% of shopping centers70 Rating of shopping centers that violate fire safety will be made in Moscow //Komsomolskaya Pravda, 16.04.2018: https://www.msk.kp.ru/daily/26819.5/3856564/..

One of the most important conditions for improving the efficiency of public control measures is the establishment of clear rules for their implementation – the development of methods for the implementation of each of the forms of public control provided by the law, the approval of standard forms of final documents drawn up as a result of the activities, without excessive formalization of this work.
So far, we cannot say that Russia has developed a clear and operational system of public control. The main drawbacks include poor awareness of citizens about the possibilities and subjects of public control, poor coordination of public inspectors with regional and local governments, restricted access to the inspected data (in particular, in the field of environmental control), finally, the lack of sufficient powers of public inspectors and effective norms of responsibility for ignoring the results of public control.
One of the most important conditions for improving the efficiency of public control measures is the establishment of clear rules for their implementation – the development of methods for the implementation of each of the forms of public control provided by the law, the approval of standard forms of final documents drawn up as a result of the activities, without excessive formalization of this work.
The lack of opportunities to draw high-quality professionals ensuring the efficient control is a relevant problem. The main objective is not the fixed status of public inspectors and experts, or their one-time involvement in assessing the situation in a socially significant sphere, but constant cooperation related to large amount of work. In the field of environmental protection under public pressure, the status of subjects of control was legally fixed, the procedure for the implementation of public environmental control and interaction of public inspectors with public councils of state forest and environmental supervision bodies was established. This kind of legal basis should be created for those involved in the protection of public order, voluntary fire services. The issue of empowering public inspectors to carry out inspections in places of mass stay of people, whether private, municipal or public facilities, remains particularly urgent.
The issue of expansion of the sphere of public control remains open. In particular, civil activists have repeatedly advocated for the legislative consolidation of the possibility of public control not only for the activities of governments and other bodies and organizations vested with separate public powers, but also for economic entities: utilities, major banks, rail and air carriers, etc. However, the representatives of the Ministry of Internal Affairs, the Prosecutor General’s Office and the Investigative Committee, who took part in the discussion of this issue in the Civic Chamber of the Russian Federation, are totally against it, arguing that in this case there will be an intersection of the powers of state and municipal control bodies and and public control bodies71 The Civic Chamber of the Russian Federation proposes to legislatively fix the accurate mechanism of public control activities // GARANT.RU, 16.08.2018: http://www.garant.ru/news/1213883/#ixzz5XOvfPjjL ..
Certain legislative gaps remain. The development of the model bill “On public control in the subject region of the Russian Federation”, methodical recommendations on implementation of public control in the system of local government is extremely relevant.
An important institution of civil society is the media, meant to cover the problems the citizens are concerned about. Today the media gradually lose this social role. This can be attributed to a number of reasons, but one of the major reasons is general crisis of traditional media, which lose to social media in the fight for the audience. In this situation, the media are forced to adapt to the existing situation, to cover the so-called hot news, sensations, almost without paying attention to quality investigations and social issues – it is well known that the negative news is easier to sell, and the media today are put in such conditions that they are trying to earn literally from everything72 “In pursuit of profit the media forgot about social responsibility — Yevgeny Primakov//Website of the Civic Chamber of the Russian Federation, 29.03.2018: https://www.oprf.ru/press/news/2018/newsitem/44730.. In the regions there are successful practices of media covering social issues, their presentation was held at the meeting of the expert Council “For social responsibility of media” of the national award “Media Manager of Russia – 2018” in the Civic Chamber of the Russian Federation73 Not for the sake of ratings: Media covering social issues presented their projects to the Civic Chamber of the Russian Federation // Website of the Civic Chamber of the Russian Federation, 26.06.2018: https://www.oprf.ru/press/news/2018/newsitem/45803.. The final “Community” Forum in Moscow presented a successful example of the Republic of Komi, where the public with the support of the regional Civic Chamber implemented a project of cooperation with regional media. In order to support socially responsible regional media, the Civic Chamber of the Russian Federation plans to launch an educational platform for them, where professionals of the federal mass media will share positive developments and tell how to become competitive in the conditions of digital development of the country74 “The NPO are not yet very good at communicating with the media and do not pay due attention to it” — Konstantin Komkov//Website of the Civic Chamber of the Russian Federation, 23.05.2018: https://www.oprf.ru/press/news/2018/newsitem/45367. .
In November 2017, the Regional Media Coordination Council was created at the Civic Chamber. It is noted that the situation of regional media deteriorates due to changes in the conditions of delivery of periodicals to readers. In early 2018, a number of regional media received a draft additional agreement from the Interregional Subscription Agency, under the terms of which the publisher is obliged to ensure the delivery of the circulation to newspaper and magazine distribution points on its own and at its own expense, in other words, to assume the responsibility for the transportation within the subject region of the Russian Federation, taking into account that the cost of delivery has already been included in the subscription price in fact, it is proposed to pay for these services another time75 Check the Russian Post: is it legal to pay for subscription/twice/Website of the Civic Chamber of the Russian Federation, 07.03.2018: https://www.oprf.ru/press/news/2018/newsitem/44417.. The Civic Chamber of the Russian Federation has already appealed to the FAS on the issue of double fees that the Russian Post sets in the regions.
Within the framework of activities of the Civic Chamber of the Russian Federation the issue of digital inequality has been repeatedly raised: despite the almost 80% level of Internet penetration in the country76 The audience of Runet is growing again // Vedomosti, 17.01.2018: https://www.vedomosti.ru/technology/articles/2018/01/17/748042-auditoriya-runeta-rastet., digital access in Moscow is much better than in small towns and villages in remote areas77 Another Internet: digitalization of small towns in Russia//A. A. Vysokovsky High School of Urban Studies, 2018: https://urban.hse.ru/news/220104443.html.. This issue is crucial from the point of view of the unity of our country, in 2019 the Civic Chamber plans to launch a hotline public control on the quality of communications and Internet in the regions. In addition, the issue of providing a legislative framework for fixed assignment of the “22nd button” in local cable networks to the leading local TV companies was raised the Website of the Civic Chamber. The point is that within the basic package of TV channels there should be a local channel broadcasting local news. On this account, there is a special order of the President of Russia “to consider the feasibility of determining the mandatory public TV channel for each municipality and broadcasting such TV channel on the 22nd position in the communication networks”78 The Media Commission of the Civic Chamber of the Russian Federation supports the idea of assigning the 22 button in cable networks to the local city channels//Website of the Civic Chamber of the Russian Federation, 25.04.2018: https://www.oprf.ru/press/news/2018/newsitem/45074., but the situation is not yet resolved.

The situation of the industry makes it difficult to balance legislation and administrative practices with respect to traditional media and bloggers. The media undergo endless inspections, while bloggers are not limited to such rigid framework of the law79 What prevents the NPO to communicate effectively with the media? The Civic Chamber of the Russian Federation will clarify it during monitoring //Website of the Civic Chamber of the Russian Federation, 17.04.2018: https://www.oprf.ru/press/news/2018/newsitem/44942.. Therefore, the need to legitimate the profession of a blogger is a long pending issue80 “Western social media themselves decide who, when and how to “demolish”, while we play in liberalism” — Alexander Malkevich//Website of the Civic Chamber of the Russian Federation, 09.06.2018: https://www.oprf.ru/press/news/2018/newsitem/45611.. Moreover, in the field of electronic media and social media there are ambiguous processes associated with the uncontrolled spread of unreliable content. Fake news is purposefully launched to make them public in “x hour”81 “Many bloggers will do anything to regain their followers and their likes” — Alexander Malkevich//Website of the Civic Chamber of the Russian Federation, 11.07.2018: https://www.oprf.ru/press/news/2018/newsitem/45978.. The situation is all the more ambiguous, as most of the social media used by Russians are not in the Russian jurisdiction and block the accounts at their discretion.